In very simple terms, e-commerce logistics is the process of getting products from a seller’s warehouse to a customer’s doorstep. The goal of any e-commerce company is to provide customers with fast and affordable shipping options. Achieving this requires a robust logistics and fulfilment process. This involves efficient inventory management, strategic warehousing, and seamless coordination with shipping carriers. A well-executed logistics strategy not only reduces costs but also improves delivery times and reliability, giving companies a competitive edge in the market.
Depending on the industry, logistics generally includes the following steps:
- Procuring supplies
- Managing inventory
- Accepting orders
- Packaging & Order shipment
- Handling returns
Compared to traditional brick-and-mortar retailing, e-commerce involves additional logistical elements, such as managing online interactions and responding to rapidly shifting demands in the online marketplace. Unlike traditional retail, where sales occur through physical store visits, e-commerce sales happen online, which opens up a variety of fulfilment options.
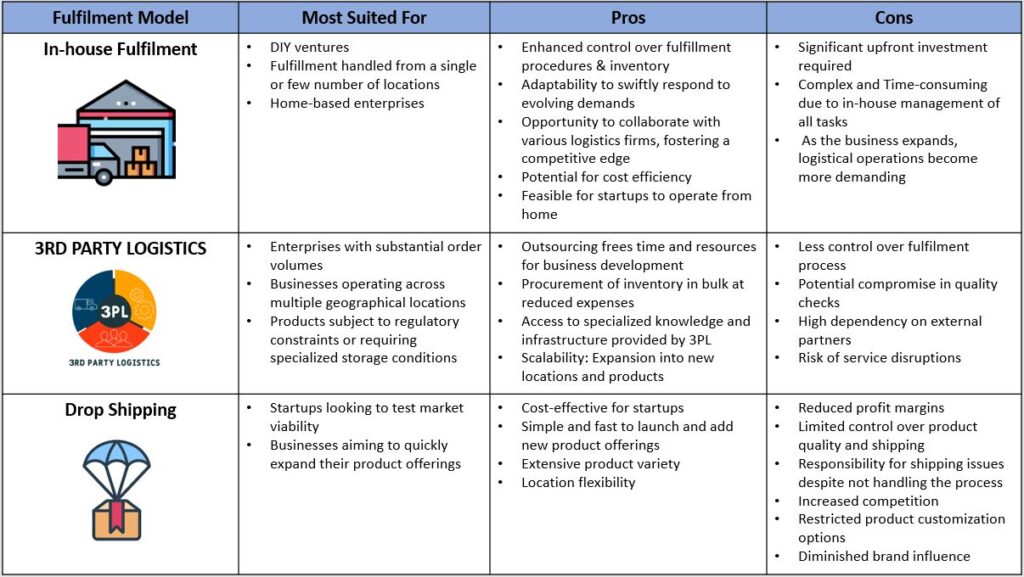
Fulfilment Models
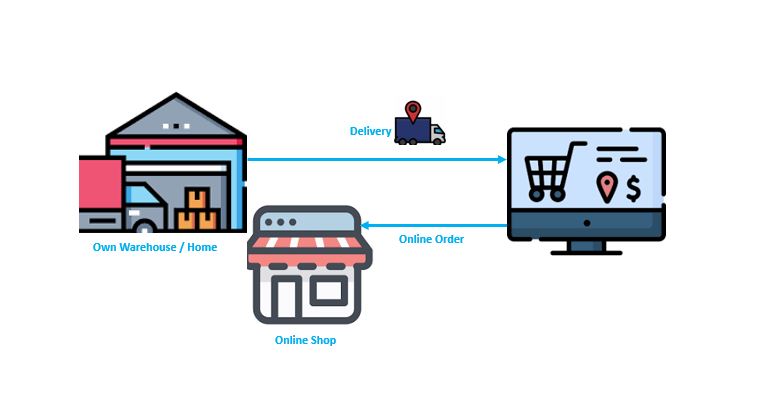
In-house Fulfilment: In this model, the retailer/business handles every aspect of the fulfilment process internally. This includes storing inventory, processing orders, and shipping directly from their own facilities. While it is similar to traditional retail fulfilment, the key difference is that all interactions and transactions occur online, without any physical customer presence in the store. Although this approach allows the retailer to maintain complete control over the fulfilment process, ensuring quality, it requires substantial resources and infrastructure to manage effectively.
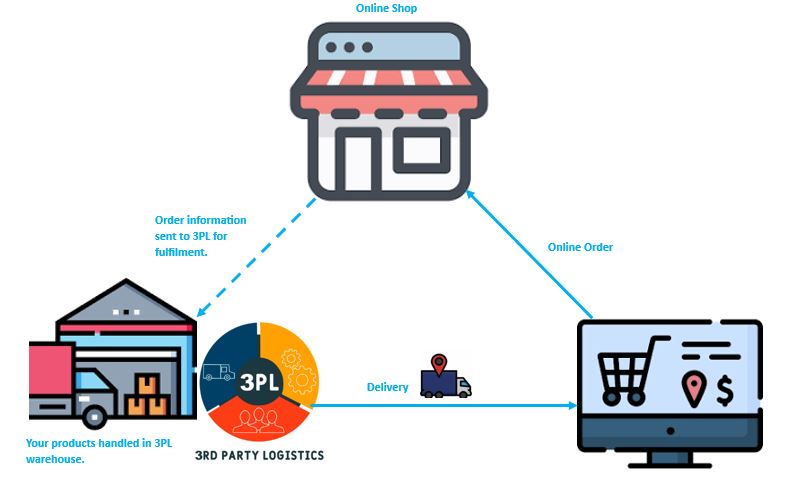
Third-party Logistics (3PL): In this model, retailers outsource their fulfilment operations to third-party logistics providers. These specialized providers take charge of crucial tasks such as warehousing, inventory management, and shipping on behalf of the retailer. This approach is particularly favoured by businesses with ambitious expansion plans seeking scalability. Moreover, companies aiming to penetrate new markets often partner with a 3PL to expedite their establishment process in those regions. By leveraging the expertise and resources of a 3PL, retailers can focus on core business activities while benefiting from streamlined logistics operations and broader market reach offered by the 3PL
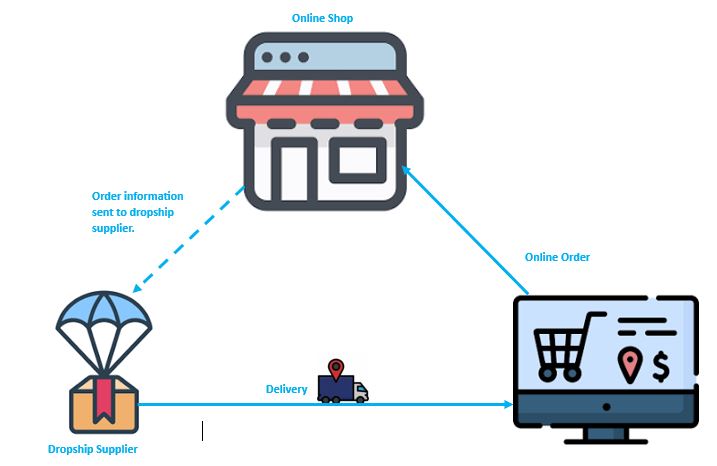
Dropshipping: In this model, retailers establish partnerships with suppliers who directly ship products to customers upon receiving orders. When an order is placed, the supplier handles the shipping process directly on behalf of the retailer. Additionally, retailers have the option to incorporate their branding on the products, typically for an additional cost. Unlike traditional retail models, the retailer does not need to maintain inventory; instead, they solely manage order processing and customer service. Dropshipping offers retailers the advantage of reduced overhead costs and inventory management responsibilities, allowing them to focus on marketing efforts and enhancing customer experience.
Some retailers blend aspects of various fulfilment models to devise a hybrid approach tailored to their unique requirements. For instance, a retailer may opt for in-house fulfilment for select products, while employing dropshipping for others.
Furthermore, in service industries, there exists the concept of Crowdsourced Fulfilment. This model harnesses a network of independent contractors or local businesses to fulfill orders, often facilitating same-day or hyper-local deliveries. Uber and Instacart are examples of this approach’s effectiveness and popularity.
The choice of fulfilment model is influenced by the characteristics of your product as well as your business vision and growth objectives.
Handling Returns
When selecting a fulfilment model, it’s important to remember that free shipping and returns are highly attractive to online shoppers. Therefore, it’s wise to incorporate these costs into your product pricing from the outset and promote this feature as a key aspect of your store, or plan to introduce it strategically when the opportunity arises. Determination of free shipping charges also depends on your product selection. For instance, If your product is niche and you are targeting high income customers, they would not mind paying additional shipping charges. This can be determined during Market Research process.
Handling returns can be one of the most challenging aspects of e-commerce logistics for startups. However, returns are inevitable. According to Transport Topics, the average return rate for e-commerce is 17.6 % at the end of 2023. This highlights the importance of managing returns as effectively as product deliveries.
Effective return management boosts customer confidence, assuring them that they won’t be stuck with products that don’t meet their needs. This confidence encourages purchases, and if your products meet their expectations, returns will be minimized.
Quickly processing returns and issuing refunds not only keeps customers satisfied but also allows you to quickly reintegrate returned stock into your inventory. This enables you to either liquidate or resell returned items that are not damaged.
Ideally, return management should be separate from deliveries and handled by a dedicated individual or a small team to ensure a seamless supply chain.
Consider the following factors when improving your return process:
- Will you cover the cost of return shipping?
- Will you resell returned products?
- Will you liquidate returned items?
By addressing these questions, you can develop a strategy to enhance the delivery experience for your customers.
Supplier Strategy
Your business relies significantly on your supplier for raw materials or finished products. When selecting suppliers, consider these key factors:
- Is the quality of the product satisfactory?
- Does the supplier consistently meet delivery deadlines?
- How do the supplier’s prices compare with others in the market?
- Are there any minimum order quantity requirements?
- What is the supplier’s policy on returns for damaged goods?
- What are the delivery charges, and where is the supplier located?
It’s wise to avoid relying solely on a single supplier. Instead, establish relationships with multiple suppliers to safeguard against potential supply disruptions.
Delivery setup
If you choose to handle fulfilment in-house, you’ll need a shipping partner to deliver your orders. These partners usually include logistics companies like FedEx, DHL, or local carriers/couriers in your area. When selecting shipping partners, consider the following factors:
- Timeliness and reliability of deliveries
- Choice of shipping options, such as standard or express delivery
- Shipping costs
- Geographic coverage, ensuring they service all current and tracking delivery areas
- Tracking capabilities
- Quality of customer service
- Efficiency in handling customer returns
Like with suppliers, it’s wise not to depend on a single shipping partner. Instead, establish relationships with multiple partners to ensure business continuity in case there are service issues with one partner.
In conclusion, mastering the intricacies of e-commerce logistics is essential for the success of any online business. From procuring supplies to managing inventory, through to handling delivery and returns, every step in the process plays a crucial role in satisfying customers and ensuring business growth. The choice of fulfilment model depends on various factors such as product characteristics, business vision, and growth objectives. Regardless of the chosen model, prioritizing fast and affordable shipping options, along with efficient return management, is key to meeting customer expectations and building trust. By optimizing e-commerce logistics, businesses can not only reduce costs and improve delivery times but also gain a competitive edge in the dynamic online marketplace.
This topic is part of a blog series. In case you have missed the previous posts, here they are:
How To Launch Your Online Business: From Concept To Cart
Best Products to Sell Online: Expert Product Selection Strategies
